PtxNi10−xO nanoparticles supported on N-doped graphene oxide with a synergetic effect for highly efficient hydrolysis of ammonia borane†
Abstract
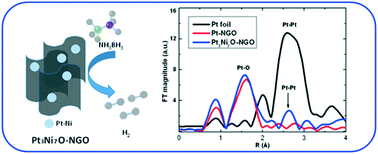
Oxidized Pt–Ni nanoparticles were deposited on N-doped graphene oxide (NGO) for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane (AB). The optimized Pt3Ni7O–NGO sample shows a high total turnover frequency (TOF) value of 709.6 mol H2 per mol Cat-Pt per min in the hydrolysis of AB, which is one of the best values for Pt-based catalysts to date. Moreover, when calculating all metal contents (mainly Ni, Pt : Ni = 1 : 5) in the hybrid, the total TOF value is still as high as 120.7 mol H2 per mol Cat-metal per min, better than that of pure Pt/C or Pt on NGO. The hybrid also exhibits a good stability with more than 76% activity (TOF = 544.9) after 9 cycles. Synchrotron radiation X-ray absorption spectroscopy reveals that Pt and Ni in the catalyst exhibit a strong interaction through oxygen bonds and the bimetallic structure shows further interaction with the support material. All the components in the hybrid can thus be connected to show a synergetic effect for enhanced catalytic performance. The excellent performance can be related to the unique electronic structure of the hybrid with the synergetic effect, which may also shed light on the design of high-efficiency catalysts for other energy-related applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...