CO2 hydrogenation to higher hydrocarbons on K/Fe–Al–O spinel catalysts promoted with Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, Mn and Ce†
Abstract
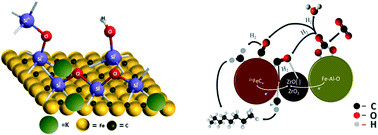
Metal oxides grafted on K/Fe–Al–O spinel precursors prepared by co-precipitation in the presence of the surfactant CTAB displayed significant effects on the performance of the catalysts in CO2 hydrogenation to hydrocarbons. Specifically, 20 wt% titania and 20 wt% zirconia increased the rates of both the reverse water gas shift reaction (RWGS) and the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FTS), as reflected in the increase of the CO2 conversion and the decrease of CO selectivity. While 20 wt% titania increased methane and C2–C4 selectivity and decreased C5+ selectivity, 20 wt% zirconia displayed no effect on methane and increased C2–C4 and C5+ selectivity. 5 wt% hafnia and 5 wt% manganese oxide had little effect on performance and 5 wt% ceria enhanced the selectivity to both methane and light C2–C4 and significantly decreased the selectivity to C5+. Silica inserted by grafting at the Fe–Al–O surface at 5 wt% acted as a promoter of CO2 conversion but at high loading of 15 wt% was a strong inhibitor to FTS, increased methane and CO selectivity and decreased CO2 conversion. Nanoparticles of both spinel and Fe-carbide phases in contact with zirconia caused a decline in the electron density of surface iron atoms, as reflected by the increase of the binding energy of Fe (2p) electrons by 0.7–0.8 eV as detected by XPS. This may be a result of a strong interaction of iron oxide and zirconia due to incorporation of Zr in the Fe–Al–O spinel structure and a strong interaction of near metallic iron in carbide nanocrystals in contact with ZrO2 nanoparticles that plays a role of an electron acceptor as a Lewis acid and explains the increase of CO2 conversion. The extremely low activity of the silica modified catalyst in FTS and enhanced activity in methanation are consistent with the model of selective blocking of the surface iron ions of the Fe-carbide component with grafted silica moieties and their interaction with the potassium promoter.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...