Evaluating the role of acidic, basic, and polar amino acids and dipeptides on a molecular electrocatalyst for H2 oxidation†
Abstract
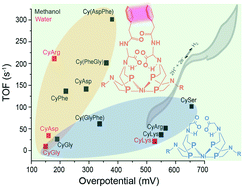
Amino acids and peptides have been shown to have a significant influence on the H2 production and oxidation reactivity of Ni(PR2NR′2)2, where PR2NR′2 = 1,5-diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctane, R is either phenyl (Ph) or cyclohexyl (Cy), and R′ is either an amino acid or peptide. Most recently, the Ni(PCy2Naminoacid2)2 complexes (CyAA) have shown enhanced H2 oxidation rates, water solubility, and in the case of arginine (CyArg) and phenylalanine (CyPhe), electrocatalytic reversibility. Both the backbone –COOH and side chain interactions were shown to be critical to catalytic performance. Here we further investigate the roles of the outer coordination sphere by evaluating amino acids with acidic, basic, and hydrophilic side chains, as well as dipeptides which combine multiple successful features from previous complexes. Six new complexes were prepared, three containing single amino acids: aspartic acid (CyAsp), lysine (CyLys), and serine (CySer) and three containing dipeptides: glycine-phenylalanine (Cy(GlyPhe)), phenylalanine-glycine (Cy(PheGly)), and aspartic acid-phenylananine (Cy(AspPhe)). The resulting catalytic performance demonstrates that complexes need both interactions between side chain and –COOH groups for fast, efficient catalysis. The fastest of all of the catalysts, Cy(AspPhe), had both of these features, while the other dipeptide complexes with an amide replacing the –COOH were both slower; however, the amide group was demonstrated to participate in the proton pathway when side chain interactions are present to position it. Both the hydrophilic and basic side chains, notably lacking in side chain interactions, significantly increased the overpotential, with only modest increases in TOF. Of all of the complexes, only CyAsp was electrocatalytically reversible at room temperature, and only in water, the first of these complexes to demonstrate room temperature aqueous electrocatalytic reversibility for the H2/H+ transformation. These results continue to provide and solidify design rules for controlling reactivity and efficiency of Ni(P2N2)2 complexes with the outer coordination sphere.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...