Fe/Fe3C@N-doped porous carbon hybrids derived from nano-scale MOFs: robust and enhanced heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation†
Abstract
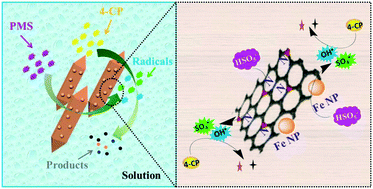
This study subtly integrates eco-friendly and cost-effective Fe-based nanoparticles (Fe/Fe3C NPs) with N-doped porous carbon (NC) to effectively activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and decompose target organic compounds in water. The Fe/Fe3C@NC hybrids can be facilely fabricated through one-pot pyrolysis of an Fe, N-containing nano-scale metal–organic framework (MOF). Benefiting from the excellent enrichment ability of NC matrix and abundant accessible sites arising from NPs and catalyst support, Fe/Fe3C@NC outperformed common oxides such as Co3O4 and Fe3O4 for PMS activation and organic compound degradation. With high saturation magnetization, the catalyst can then be easily recycled for subsequent runs without significant capacity or activity loss. The applicability of this catalyst was also systematically assessed by means of the influence of the main factors and extent of mineralization. Through the mechanistic study, the active species in the system were identified as sulfate radicals (SO4˙−) and hydroxyl radicals (OH˙), and the variable chemical valences of Fe NPs as well as pyridinic N and graphitic N in support contribute to the outstanding catalytic activity. Such findings elucidated a new opportunity for the design of a feasible platform to improve the overall catalytic activity in environmental remediation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Catalysis Science & Technology HOT Articles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...