Newly designed manganese and cobalt complexes with pendant amines for the hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol: a DFT study†
Abstract
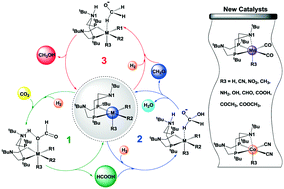
A series of manganese and cobalt complexes with pendant amines, (PtBu2NtBu2)M(R1)(R2)(R3) (M = Mn, R1 = R2 = CO; M = Co, R1 = R2 = CN; R3 = H, CN, NO2, CH3, NH2, OH, CHO, COOH, COCH3, and COOCH3), were proposed and examined as potential catalysts for the production of methanol from CO2 and H2. Detailed mechanisms with three cascade catalytic reactions, the hydrogenation of CO2 to formic acid, the hydrogenation of formic acid to formaldehyde with the formation of water, and the hydrogenation of formaldehyde to methanol, are predicted and analyzed through density functional theory calculations. Among all proposed complexes, (PtBu2NtBu2)Co(CN)2(COOH) (1Co–COOH) and (PtBu2NtBu2)Co(CN)2(NH2) (1Co-NH2) are the two most active with total free energy barriers of 24.9 and 25.0 kcal mol−1, respectively. (PtBu2NtBu2)Mn(CO)2(COOH) (1Mn–COOH) and (PtBu2NtBu2)Mn(CO)2(NO2) (1Mn-NO2) are the most active manganese complexes with total free energy barriers of 26.6 and 27.7 kcal mol−1, respectively. Such low barriers indicate that these newly designed cobalt and manganese catalysts are promising low-cost catalysts for the conversion of CO2 and H2 to methanol under mild conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...