Decreased domain size of p-DTS(FBTTh2)2/P(NDI2OD-T2) blend films due to their different solution aggregation behavior at different temperatures†
Abstract
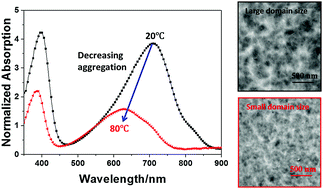
Nanoscale interpenetrating networks play a key role in determining the optoelectrical properties of functional blends. However, phase separated large domain sizes could probably be observed in pristine films composed of two crystalline components. For example, p-DTS(FBTTh2)2/P(NDI2OD-T2) 3/2 blend films with interpenetrating networks are obtained, however, large domain sizes are found when they are prepared from a 20 °C solution due to the simultaneous process of crystallization and phase separation during solvent evaporation. In this paper, we proposed to reduce the domain size of p-DTS(FBTTh2)2/P(NDI2OD-T2) blend films using their different solution aggregation behaviors at different temperatures. The aggregation of p-DTS(FBTTh2)2 molecules in chlorobenzene (CB) was insensitive to the solution temperature. However, the in situ absorption spectra of the neat P(NDI2OD-T2) solution from 80 °C to room temperature indicated that P(NDI2OD-T2) aggregation increased with decreasing temperature due to intrachain interactions. Therefore, in order to reduce the domain size, we employed a hot solution to prepare the blend films. During the solidification process, the majority of p-DTS(FBTTh2)2 molecules were confined in the P(NDI2OD-T2) networks prior to occurrence of severe p-DTS(FBTTh2)2 aggregation. Thus, the domain size of the p-DTS(FBTTh2)2 phase became smaller than that of the pristine films, leading to a decrease in the corresponding photoluminescence intensity of the blend films. In addition, the crystallinity of the blend films improved after thermal annealing, which resulted from the ordered alignment of p-DTS(FBTTh2)2 molecules facilitated by their enhanced diffusion ability. Based on the various morphologies, a possible phase diagram of the p-DTS(FBTTh2)2/P(NDI2OD-T2) blend system was depicted, which could be a guide to directly control the morphology of blend films.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...