Vesicle to micelle transition in the ternary mixture of L121/SDS/D2O: NMR, EPR and SANS studies†
Abstract
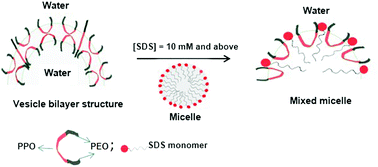
Subtle changes in the microstructure and dynamics of the triblock copolymer L121, (ethylene oxide)5 (propylene oxide)68 (ethylene oxide)5i.e., E5P68E5, and sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS) system in aqueous medium were investigated using high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) methods. NMR self-diffusion measurements helped us to understand the nature of binding of SDS with L121, and the formation of their mixed aggregates. These results showed that even at low [SDS] (∼2 mM), the addition of L121 stabilized the dynamics of SDS. Furthermore, the increase in [SDS] resulted in progressive changes in the diffusion behavior of both SDS and L121. 13C chemical shift analysis revealed that preferential binding of L121 occurred on the SDS micelle surface. Deuterium (2H) NMR spin-relaxation data evidenced that the formed mixed aggregates were non-spherical in terms of relaxation rate changes, and slowed the dynamics. The rotational correlation times of mixed aggregates were estimated from EPR analysis. A SANS study indicated the presence of uni- and multi-lamellar vesicles of L121 at low [SDS]. The vesicles transformed to mixed L121-SDS micelles in the presence of a higher [SDS]. This was supported by the measurements of 2H NMR spin-relaxation and EPR rotational correlation times.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...