The influence of the concentration and adsorption sites of different chemical groups on graphene through first principles simulations
Abstract
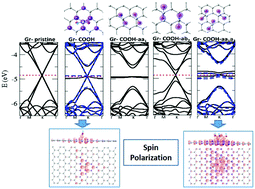
Carbon nanomaterials are one of the most promising nanostructures for adsorption of chemical species due to their high superficial area and possible interesting applications. A systematic study of chemical groups attached on graphene surfaces is necessary in order to evaluate the influence of the type and number of functionalizations on the resulting properties of a derived system. In this work, first principles simulations were used to evaluate the physical effects of different concentrations of chemical groups –COOH, –COH, –OH, –O– or –NH2 adsorbed on the graphene surface. The functionalizations occur from one up to three chemical groups and either in the same or different carbon rings. It is observed that significant changes occur in the adsorption and electronic properties due to the hybridization and symmetry points of interaction of the chemical groups. Then, the results indicate that it is possible to control the properties of the desired system through the type, concentration and binding site of the functional groups attached to the graphene monolayer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...