Ion dehydration controls adsorption at the micellar interface: hydrotropic ions
Abstract
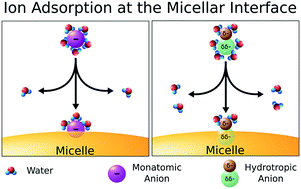
The properties of ionic micelles depend on the nature of the counterion, and these effects become more evident as the ion adsorption at the interface increases. Prediction of the relative extent of ion adsorption is required for rational design of ionic micellar aggregates. Unlike the well understood adsorption of monatomic ions, the adsorption of polyatomic ions is not easily predicted. We combined experimental and computational methods to evaluate the affinity of hydrotropic ions, i.e., ions with polar and apolar regions, to the surface of positively charged micelles. We analyzed cationic micelles of dodecyltrimethylammonium and six hydrotropic counterions: methanesulfonate, trifluoromethanesulfonate, benzenesulfonate, acetate, trifluoroacetate and benzoate. Our results demonstrated that the apolar region of hydrotropic ions had the largest influence on micellar properties. The dehydration of the apolar region of hydrotropic ions upon their adsorption at the micellar interface determined the ion adsorption extension, differently to what was expected based on Collins’ law of matching affinities. These results may lead to more general models to describe the adsorption of ions, including polyatomic ions, at the micellar interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...