Developing an efficient NiCo2S4 cocatalyst for improving the visible light H2 evolution performance of CdS nanoparticles†
Abstract
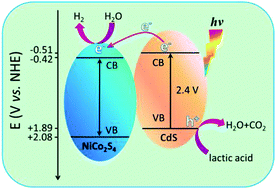
Developing efficient alternatives to the widely used Pt cocatalyst in photocatalytic H2O splitting is of great importance in view of large-scale production of clear H2 energy. Herein, we report the facile synthesis of NiCo2S4 and its first use as a highly active and cost-affordable cocatalyst to boost visible light H2 generation with the CdS semiconductor. The synthesized NiCo2S4/CdS composite materials are fully characterized by various techniques including X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), UV-Vis diffusion reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), and N2 adsorption measurements. With the optimized NiCo2S4/CdS composite sample, a high H2 generation rate of 137 μmol h−1 is obtained under visible light irradiation, which is more than 17 times higher than that of bare CdS material. The results of photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, transient photocurrent response and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy demonstrate the remarkably promoted migration and separation of photogenerated charge carriers over the heterostructured NiCo2S4/CdS material, thus leading to obviously enhanced photocatalytic performance. Moreover, a possible mechanism for the photocatalytic H2 evolution reaction is also proposed based on the observed results of activity evaluation and photoelectrochemical measurements.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...