Structure–property relationships in protic ionic liquids: a study of solvent–solvent and solvent–solute interactions
Abstract
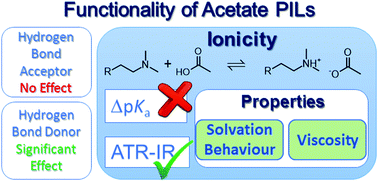
The ionic nature of a functionalized protic ionic liquid cannot be rationalized simply through the differences in aqueous proton dissociation constants between the acid precursor and the conjugate acid of the base precursor. The extent of proton transfer, i.e. the equilibrium ionicity, of a tertiary ammonium acetate protic ionic liquid can be significantly increased by introducing an hydroxyl functional group on the cation, compared to the alkyl or amino-functionalized analogues. This increase in apparent ionic nature correlates well with variations in solvent–solute and solvent–solvent interaction parameters, as well as with physicochemical properties such as viscosity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...