A rapid scan vacuum FTIR method for determining diffusion coefficients in viscous and glassy aerosol particles†
Abstract
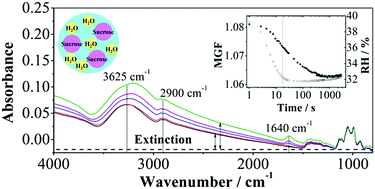
We report a new method to investigate water transport kinetics in aerosol particles by using rapid scan FTIR spectroscopy combined with a custom-built pulse relative humidity (RH) control system. From real time in situ measurements of RH and composition using high time resolution infrared spectroscopy (0.12 s for one spectrum), and through achieving a high rate of RH change (as fast as 60% per second), we are able to investigate the competition between the gas and condensed phase diffusive transport limits of water for particles with mean diameter ∼3 μm and varying phase and viscosity. The characteristic time (τ) for equilibration in particle composition following a step change in RH is measured to quantify dissolution timescales for crystalline particles and to probe the kinetics of water evaporation and condensation in amorphous particles. We show that the dissolution kinetics are prompt for crystalline inorganic salt particles following an increase in RH from below to above the deliquescence RH, occurring on a timescale comparable to the timescale of the RH change (<1 s). For aqueous sucrose particles, we show that the timescales for both the drying and condensation processes can be delayed by many orders of magnitude, depending on the viscosity of the particles in the range 101 to 109 Pa s considered here. For amorphous particles, these kinetics are shown to be consistent with previous measurements of mass transfer rates in larger single particles. More specifically, the consistency suggests that fully understanding and modelling the complex microphysical processes and heterogeneities that form in viscous particles may not be necessary for estimating timescales for particle equilibration. A comparison of the kinetics for crystalline and amorphous particles illustrates the interplay of the rates of gas and condensed phase diffusion in determining the mass transport rates of water in aerosols.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...