Fabrication of metalosomes (metal containing cationic liposomes) using single chain surfactants as a precursor via formation of inorganic organic hybrids†
Abstract
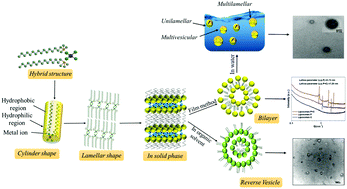
Among the self-assembled forms of surfactants, vesicles/liposomes are a highly promising and interesting feature of surfactants, which are usually formed from water insoluble surfactants. Herein, we demonstrate the formation of liposomes from single-chain cationic surfactants with the help of metals as a part of the counter ion, and these metal embedded liposomes are termed as metalosomes. It is a noteworthy advancement in the area of self-assembled molecular structures since we report the preparation of metal embedded liposomes (metalosomes) from a water soluble single chain cationic surfactant, which is otherwise a property or an arrangement made by double tailed surfactants, or more precisely lipids that are poorly water soluble. We can use this method for various cationic surfactants and metal combinations and the studies are still in process. However, this preliminary report on manganese-based surfactants depicts the successful formation of cationic metalosomes (with/without cholesterol), and the formation, structure and size has been verified using TEM, FE-SEM, DLS XRD and SAXS. The comparison of metalosomes with reverse vesicles in different solvents further gave an insight of microstructure and solvent environment effects on the self-assembly of metallosurfactants. In addition, we have also evaluated the encapsulation ability of metalosomes for fluorescein dye. High encapsulation efficiency of Mn-somes makes them promising candidates for several applications, particularly because of its water solubility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...