Aqueous dispersions of nanostructures formed through the self-assembly of iminolipids with exchangeable hydrophobic termini†
Abstract
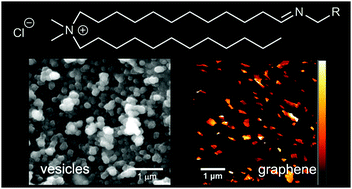
The addition of amines to an aldehyde surfactant, which was designed to be analogous to didodecyldimethylammonium bromide, gave exchangeable “iminolipids” that self-assembled to give stable aqueous dispersions of nano-sized vesicles. For example, sonication of suspensions of the n-hexylamine-derived iminolipid gave vesicles 50 to 200 nm in diameter that could encapsulate a water-soluble dye. The iminolipids could undergo dynamic exchange with added amines, and the resulting equilibrium constants (Krel) were quantified by 1H NMR spectroscopy. In the absence of lipid self-assembly, in CDCl3, the assayed primary amines gave very similar Krel values. However in D2O the value of Krel generally increased with increasing amine hydrophobicity, consistent with partitioning into a self-assembled bilayer. Amines with aromatic groups showed significantly higher values of Krel in D2O compared to similarly hydrophobic alkylamines, suggesting that π–π interactions favor lipid self-assembly. Given this synergistic relationship, π-rich pyrenyliminolipids were created and used to exfoliate graphite, leading to aqueous dispersions of graphene flakes that were stable over several months.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...