Lithiation of multilayer Ni/NiO electrodes: criticality of nickel layer thicknesses on conversion reaction kinetics†
Abstract
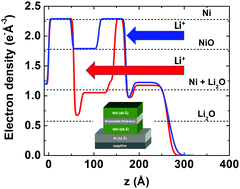
X-ray reflectivity and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used to characterize the morphological changes in thin film electrodes with alternating Ni and NiO layers during lithiation as a function of the Ni buffer layer thickness. Complete lithiation of the active NiO layers occurs only when the thickness of the Ni/NiO bilayers are less than 75 Å – a threshold value that is determined by the sum of the Ni quantity in the Ni/NiO bilayer of the multilayer stack. Thicker Ni/NiO bilayers present a kinetic barrier for lithium ion diffusion inside the stack resulting in partial lithiation of the multilayer electrodes in which only the top NiO layer lithiates. Lithiation of NiO layers in a multilayer stack also leads to an interface-specific reaction that is observed to increase the thicknesses of adjacent Ni layers by 3–4 Å and is associated with the formation of a low-density Li2O layer, corresponding to an interfacially-driven phase separation of the NiO. Rate dependent cyclic voltammetry studies reveal a linear relation between the peak current and scan rate suggesting that the lithiation kinetics are controlled by charge transfer resistance at the liquid–solid interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...