pH-Dependent absorption spectrum of a protein: a minimal electrostatic model of Anabaena sensory rhodopsin
Abstract
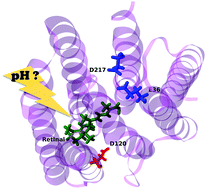
A minimal electrostatic model is introduced which aims at reproducing and analyzing the visible-light absorption energy shift of a protein with pH. It relies on the existence of a protein structure, the prediction of titratable amino-acid pKa values and a very limited set of parameters. Applied to the case of the photochromic Anabaena sensory rhodopsin protein, the model succeeds in reproducing qualitatively the reported experimental data, confirming the importance of aspartic acid 217 in the observed blue shift in the λmax of ASR at neutral pH. It also suggests for the first time the role of two other amino acids, glutamic acid 36 at basic pH and aspartic acid 120 at acidic pH.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...