Spacer-controlled emission of randomly oriented fluorophores enhanced with surface plasmon-polaritons†
Abstract
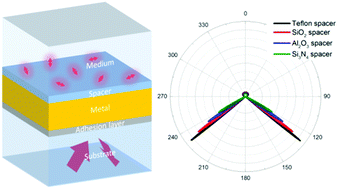
In surface plasmon-polariton enhanced fluorescence, the use of spacers is simply understood to control the distance between the fluorescence dyes and metals to avoid quenching. However, the presence of a spacer layer over the metallic surface not only manipulates the quantum yield, but also affects the surface plasmon-polariton resonance, which in turn modifies the florescence excitation rate as well as the far-field radiation pattern of the emission. This study presents a systematic investigation on the spacer-controlled emission of randomly oriented emitters in the Kretschmann configuration, with the full leverage of the coupled transfer matrix, reciprocity and plane-wave decomposition methods. It demonstrates that the introduction of a spacer between the metal film and fluorescence dyes decreases the excitation rate. Furthermore, the excitation rate decreases more for spacers with a higher refractive index due to the reduction of the effective power that goes into the resonance excitation. Combining the excitation rate with the quantum yield and photon-collection efficiency, the detected fluorescence enhancement from either the medium side or substrate side is determined and optimized for the spacer thickness and material. It was found that the highest enhancement of a randomly oriented fluorophore's emission was generally achieved in detection from the substrate side with a low refractive index spacer (e.g. Teflon and SiO2). In addition, the substrate-side measurements were thought to benefit from highly directional radiation and a more stable enhancement compared to the medium-side measurements. Our results clearly reveal physical insights into the spacer-controlled emission and provide concrete guidance in the design and measurement of fluorescence-based sensing and imaging systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...