Oligomerization process of Bcl-2 associated X protein revealed from intermediate structures in solution†
Abstract
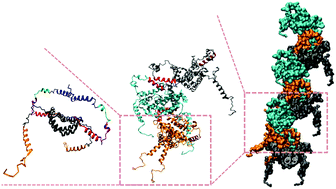
Upon apoptotic stress, Bcl-2 associated X (BAX) protein undergoes conformational changes and oligomerizes, leading to the mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and cell death. While structures of the resultant oligomer have been extensively studied, little is known about the intermediates that describe the reaction pathway from the inactive monomers to activated oligomers. Here we characterize the intermediate structures of BAX using combined small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) with on-line gel-filtration and electron spin resonance (ESR). The intermediates, including monomers, dimers, and tetramers, are reconstructed via integrating the SAXS-envelopes and ESR-determined skeleton structures. The hence revealed structures suggest a linear oligomerization of BAX utilizing the extended dimers with the two flexible α6 chains protruded out as ditopic ligands. The results of molecular dynamics simulation also support the ditopic dimer conformation with mobile α6. The ditopic dimers could further wind into a helical rod structure with three dimers in one helical turn. Our results not only reveal the on-pathway intermediates, but also suggest a ditopic oligomerization mechanism that may bridge the observed intermediate structures in solution to the large BAX assemblies lately observed on mitochondria.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...