Stability, and optical and electronic properties of ultrathin h-BNC†
Abstract
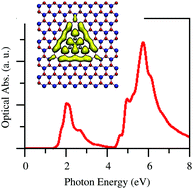
Spin polarized density functional theory has been used to study the stability, and electronic and optical properties when BN nanodomains are embedded in graphene and carbon patches are embedded in a single layer of h-BN forming h-BNC nanosystems. Our results show that graphene doped with BN nanodomains exhibits a non-zero gap, which depends on the nanodomain's shape and width. For h-BN with C domains we observe that we can tune the h-BN gap into the visible region, making the h-BNC a promising material for catalysis using solar energy. Furthermore, n-type and p-type semiconductors can be obtained by controlling the bond (C–N or C–B) in the border of the domain. These findings open the possibility to use h-BNC nanosheets for future applications in photocatalysis and optoelectronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...