A common mechanism for coenzyme cobalamin-dependent reductive dehalogenases†
Abstract
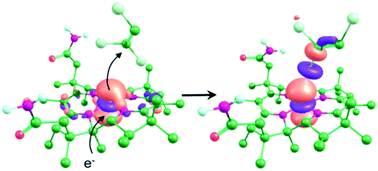
Distinct mechanisms have been proposed for the biological dehalogenation catalyzed by cobalamin-dependent enzymes, with two recent crystallographic studies suggesting different mechanisms based on the observed interaction between the organohalide substrate and cobalamin. In one case, involving an aromatic dibromide substrate in NpRdhA, a novel CoII–Br interaction was observed using EPR, suggesting a mechanism involving a [Co⋯X⋯R] adduct. However, in the case of trichloroethylene in PceA, a significantly longer Co–Cl distance was observed in X-ray crystal structures, suggesting a dissociative electron transfer mechanism. Subsequent DFT models of these reactions have not reproduced these differences in binding modes. Here, we have performed molecular docking and DFT calculations to investigate and compare the interaction between different organohalides and cobalamin in both NpRdhA and PceA. In each case, despite differences in binding in the CoII state, the reaction likely proceeds via formation of a [Co⋯X⋯R] adduct in the CoI state that weakens the breaking carbon–halide bond, suggesting this could be a general mechanism for cobalamin-dependent dehalogenation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...