Steric effect on excimer formation in planar Pt(ii) complexes†
Abstract
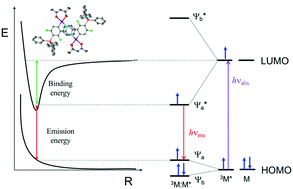
In order to understand the steric influence on excimer formation in square planar metal complexes, three different Pt(II) complexes were prepared by modifying the substituents in the main ligand: Pt(II)(dfppy)(acac) (Pt-1, where dfppy is difluorophenylpyridine, acac is acetylacetonate); the bulky triphenyl silyl (Ph3Si–) group was substituted at the pyridine moiety (Pt-2) and at the phenyl moiety (Pt-3) of the main ligand of Pt-1. The Pt-complexes showed sky-blue emission at ∼460 nm. In addition, Pt-1 and Pt-3 showed excimer emission at ∼600 nm in the concentrated solution and the solid sample. The emission lifetimes and intensities for monomeric Pt-1 and Pt-3 showed strong concentration dependence. Indeed, the lifetime of the monomer was reduced in highly concentrated solutions due to excimer formation. The intrinsic emission lifetimes were determined as 364 ns (Pt-1) and 300 ns (Pt-3) by Stern–Volmer analysis, considering the self-quenched lifetime of monomer emission. Pt-2 did not show any excimer emission in the concentrated solution or solid sample. The crystal structures of Pt-1 and Pt-3 were analysed by X-ray crystallographic measurements. The results revealed that the LUMO moiety closely overlapped with that of another Pt-complex. In this study, based on the influence of steric hindrance of the bulky Ph3Si group, we concluded that the LUMO–LUMO interaction between the pyridine moieties of the main ligand is the main factor responsible for excimer formation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...