Detection of electron tunneling across plasmonic nanoparticle–film junctions using nitrile vibrations†
Abstract
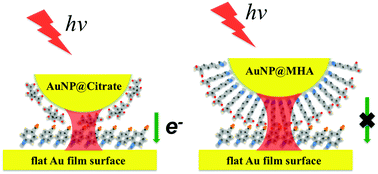
The significant electric field enhancements that occur in plasmonic nanogap junctions are instrumental in boosting the performance of spectroscopy, optoelectronics and catalysis. Electron tunneling, associated with quantum effects in small junctions, is reported to limit the electric field enhancement. However, observing and quantitatively determining how tunneling alters the electric fields within small gaps is challenging due to the nanoscale dimensions and heterogeneity present experimentally. Here, we report the use of a nitrile probe placed in the nanoparticle–film gap junctions to demonstrate that the change in the nitrile stretching band associated with the vibrational Stark effect can be directly correlated with the local electric field environment modulated by gap size variations. The emergence of Stark shifts correlates with plasmon resonance shifts associated with electron tunneling across the gap junction. Time dependent changes in the nitrile band with extended illumination further support a build up of charge associated with optical rectification in the coupled plasmon system. Computational models agree with our experimental observations that the frequency shifts arise from a vibrational Stark effect. Large local electric fields associated with the smallest gap junctions give rise to significant Stark shifts. These results indicate that nitrile Stark probes can measure the local field strengths in plasmonic junctions and monitor the subtle changes in the local electric fields resulting from electron tunneling.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...