Partitioning of caffeine in lipid bilayers reduces membrane fluidity and increases membrane thickness
Abstract
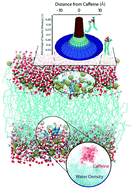
Caffeine is a small amphiphilic molecule, which is widely consumed as a stimulant to prevent fatigue, but is also used as a common drug adjuvant in modern medicine. Here, we show that caffeine interacts with unsaturated lipid membranes made of 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC). By combining X-ray diffraction and molecular dynamics simulations, we present evidence that caffeine partitions in lipid membranes and locates at the head group–tail group interface of the bilayers. By attracting water molecules from neighboring lipid molecules, it leads to the formation of “water pockets”, i.e., a local increase of water density at this interface. Through this mechanism, caffeine leads to an overall decrease of the gauche defect density in the membranes and an increase of membrane thickness, indicating a loss of membrane fluidity. These non-specific membrane interactions may increase the efficacy of analgesic drugs through changes in the bioavailability and rate of metabolism of these drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...