Microsolvation of the pyrrole cation (Py+) with nonpolar and polar ligands: infrared spectra of Py+–Ln with L = Ar, N2, and H2O (n ≤ 3)†
Abstract
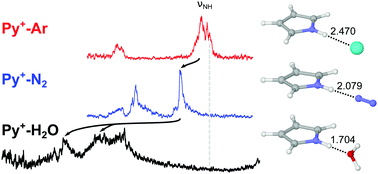
The solvation of aromatic (bio-)molecular building blocks has a strong impact on the intermolecular interactions and function of supramolecular assemblies, proteins, and DNA. Herein we characterize the initial microsolvation process of the heterocyclic aromatic pyrrole cation (Py+) in its 2A2 ground electronic state with nonpolar, quadrupolar, and dipolar ligands (L = Ar, N2, and H2O) by infrared photodissociation (IRPD) spectroscopy of cold mass-selected Py+–Ln (n ≤ 3) clusters in a molecular beam and dispersion-corrected density functional theory calculations at the B3LYP-D3/aug-cc-pVTZ level. Size- and isomer-specific shifts in the NH stretch frequency (ΔνNH) unravel the competition between various ligand binding sites, the strength of the respective intermolecular bonds, and the cluster growth. In Py+–Ar, linear H-bonding of Ar to the acidic NH group (NH⋯Ar) is competitive with π-stacking to the aromatic ring, and both Py+–Ar(H) and Py+–Ar(π) are observed. For L = N2 and H2O, the linear NH⋯L H-bond is much more stable than any other binding site and the only observed binding motif. For the Py+–Ar2 and Py+–(N2)2 trimers, the H/π isomer with one H-bonded and one π-bonded ligand strongly competes with a 2H isomer with two bifurcated nonlinear NH⋯L bonds. The latter are equivalent for Ar but nonequivalent for N2. Py+–H2O exhibits a strong and linear NH⋯O H-bond with charge-dipole configuration and C2v symmetry. IRPD spectra of cold Py+–H2O–L clusters with L = Ar and N2 reveal that Ar prefers π-stacking to the Py+ ring, while N2 forms an OH⋯N2 H-bond to the H2O ligand. The ΔνNH frequency shifts in Py+–Ln are correlated with the strength of the NH⋯L H-bond and the proton affinity (PA) of L, and a monotonic correlation between ΔνNH of the Py+–L(H) dimers and PA is established. Comparison with neutral Py–L dimers reveals the strong impact of the positive charge on the acidity of the NH group, the strength of the NH⋯L H-bond, and the preferred ligand binding motif.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...