Optimization of highly sensitive YAG:Cr3+,Nd3+ nanocrystal-based luminescent thermometer operating in an optical window of biological tissues
Abstract
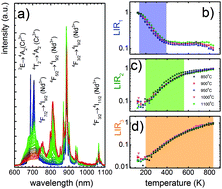
Luminescent and temperature sensitive properties of YAG:Cr3+,Nd3+ nanocrystals were analyzed as a function of temperature, nanoparticle size, and excitation wavelength. Due to numerous temperature-dependent phenomena (e.g. Boltzmann population, thermal quenching, and inter-ion energy transfer) occurring in this phosphor, four different thermometer definitions were evaluated with the target to achieve a high sensitivity and broad temperature sensitivity range. Using a Cr3+ to Nd3+ emission intensity ratio, the highest 3.48% K−1 sensitivity was obtained in the physiological temperature range. However, high sensitivity was compromised by a narrow sensitivity range or vice versa. The knowledge of the excitation and temperature susceptibility mechanisms enabled wise selection of the spectral features found in luminescence spectra for a temperature readout, which enabled the preservation of relatively high temperature sensitivity (>1.2% K−1 max) and extended the temperature sensitivity range from 100 K to 850 K. The size of the nanophosphors had negligible impact on the performance of the studied materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...