Molecular modeling and structural characterization of a high glycine–tyrosine hair keratin associated protein†
Abstract
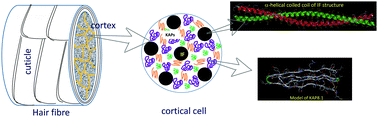
High glycine–tyrosine (HGT) proteins are an important constituent of the keratin associated proteins (KAPs) present in human hair. The glassy state physics of hair fibres are thought to be largely regulated by KAPs, which exist in an amorphous state and are readily affected by environmental conditions. However, there are no studies characterizing the individual KAPs. In this paper, we present the first step to fill this gap by computational modeling and experimental studies on a HGT protein, KAP8.1. In particular, we have modeled the three-dimensional structure of this 63-residue protein using homology information from an anti-freeze protein in snow flea. The model for KAP8.1 is characterized by four strands of poly-proline II (or PPII) type helical secondary structures, held together by two cysteine disulphide bridges. Computer simulations confirm the stability of the modelled structure and show that the protein largely samples the PPII and β-sheet conformations during the molecular dynamics simulations. Spectroscopic studies including Raman, IR and vibrational circular dichroism have also been performed on synthesized KAP8.1. The experimental studies suggest that KAP8.1 is characterised by β-sheet and PPII structures, largely consistent with the simulation studies. The model built in this work is a good starting point for further simulations to study in greater depth the glassy state physics of hair, including its water sorption isotherms, glass transition, and the effect of HGT proteins on KAP matrix plasticization. These results are a significant step towards our goal of understanding how the properties of hair can be affected and manipulated under different environmental conditions of temperature, humidity, ageing and small molecule additives.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...