Cross-sectional analysis of the core of silicon microparticles formed via zinc reduction of SiCl4†
Abstract
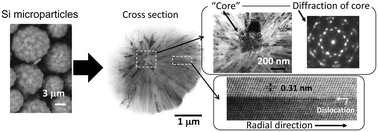
Silicon microparticles were formed by reduction of silicon tetrachloride by zinc. Chemical etching of these microparticles produced microparticles with a unique trench structure that showed visible photoluminescence. While we have previously reported the radially developed crystalline structure inside the as-synthesized microparticles, their crystalline structure was not clearly understood. In this study, we directly observed the cross sections of microparticles using a transmission electron microscope. We revealed the existence of a core inside the microparticles. The core showed a well-ordered electron diffraction pattern, which was readily explained by five single crystals rotated by 72° each. We also found that the observed radial lines and bands in the microparticles were caused by dislocations, mainly along the {111} planes. We consider that preferential etching along these radial dislocations is the origin of the formation of microparticles with trench structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...