Cd(ii) coordination polymers constructed with a flexible carboxylate linker and pyridyl co-linkers: variation in the network topologies and photoluminescence properties†
Abstract
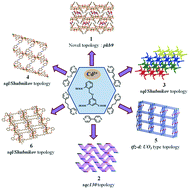
Six new coordination polymers (CPs) of Cd(II), {[Cd3(L)2(H2O)5(μ-H2O)]·6H2O}n (1), {[Cd3(L)2(4,4′-bpy)3(H2O)2]·4(H2O)·(DEF)}n (2), {[Cd(HL)(dpe)0.5(H2O)]2·(H2O)}n (3), {[Cd(HL)(dpd)0.5(H2O)]}n (4), {[Cd(HL)(1,2-dpe)0.5]}n (5), and {[Cd3(L)2(1,3-dpp)2]·3H2O}n (6) (where H3L = 5-(2-carboxybenzyloxy)isophthalic acid, 1,3-dpp = 1,3-di(4-pyridyl)propane, 1,2-dpe = 1,2-di(4-pyridyl)ethane, dpd = 1,2-di(pyridin-4-yl)diazene, dpe = 1,2-di(4 pyridyl)ethylene, and 4,4′-bpy = 4,4′-bipyridyl), were synthesized under solvothermal/hydrothermal conditions and structurally characterized via elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy, and single-crystal and powder X-ray diffraction. Compound 1 displays infinite 2D sheets, which stack upon each other to form a supramolecular 3D network. Topologically, the network can be viewed as a 3,3,3,5-connected four nodal net, which was assigned to a novel topological type, pkb9. Compound 2 shows a 3D assembly with the 3,4,6-connected topology sqc130. Compound 3 and 4 form interdigitated 3D supramolecular networks with a 4-connected sql/Shubnikov topology. Compound 5 shows an unusual 2D → 3D framework with a 3,8-connected tfz-d; UO3 topology. In compound 6, 2D → 3D packing was observed due to weak C–H⋯O interactions that aided in the formation of a 3D network with a 4-connected sql/Shubnikov topology. The luminescence properties of all the compounds in their solid state and as emulsions in various solvents were investigated using nitroaromatic compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...