Ligand-based reduction of nitrate to nitric oxide utilizing a proton-responsive secondary coordination sphere†
Abstract
Utilizing the proton-responsive pyridinediimine ligand [(2,6-iPrC6H3)(N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CMe)(N(iPr)2C2H4)(N
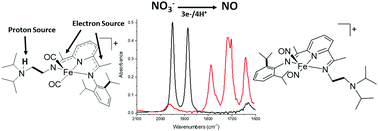
CMe)(N(iPr)2C2H4)(N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CMe)C5H3N] (didpa), the ligand-based reduction of nitrate (NO3−) to nitric oxide (NO) was achieved. The bioinspired [Fe(Hdidpa)(CO)2]+ was shown to react with tetrabutylammonium nitrate to form the dinitrosyl iron complex [Fe(didpa)(NO)2]+. The didpa scaffold was shown to provide two electrons for the net reduction of NO3− to NO in 43% yield.
CMe)C5H3N] (didpa), the ligand-based reduction of nitrate (NO3−) to nitric oxide (NO) was achieved. The bioinspired [Fe(Hdidpa)(CO)2]+ was shown to react with tetrabutylammonium nitrate to form the dinitrosyl iron complex [Fe(didpa)(NO)2]+. The didpa scaffold was shown to provide two electrons for the net reduction of NO3− to NO in 43% yield.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...