An electrochemiluminescence biosensor for Kras mutations based on locked nucleic acid functionalized DNA walkers and hyperbranched rolling circle amplification†
Abstract
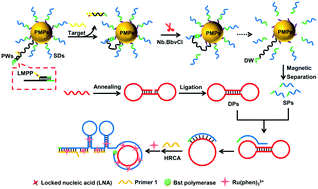
Herein, an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) biosensor for ultrasensitive and specific detection of Kras mutant genes has been developed on the basis of the high discrimination capability of locked nucleic acid (LNA) and dual signal amplification techniques including DNA walkers and hyperbranched rolling circle amplification (HRCA).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...