Synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of hydrolytically degradable materials based on aliphatic polyesters and polycarbonates
Abstract
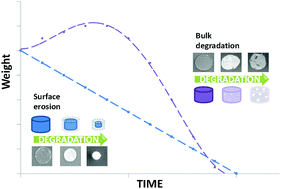
Polyester-based polymers represent excellent candidates in synthetic biodegradable and bioabsorbable materials for medical applications owing to their tailorable properties. The use of synthetic polyesters as biomaterials offers a unique control of morphology, mechanical properties and degradation profile through monomer selection, polymer composition (i.e. copolymer vs. homopolymer, stereocomplexation etc.) and molecular weight. Within this review, the synthetic routes, degradation modes and application of aliphatic polyester- and polycarbonate-based biomaterials are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...