An ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry method for the detection of steroidal glycoalkaloids in potato samples
Abstract
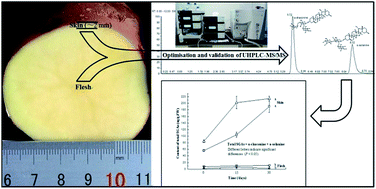
An ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) method has been optimized and validated to simultaneously monitor steroidal glycoalkaloids (SGAs), α-chaconine and α-solanine, in potato samples stored under natural indoor conditions in Kunming. Two different analytical columns (Hypersil Gold C18 and ZORBAX RRHD HILIC Plus) were assessed. The ZORBAX RRHD HILIC Plus showed better separation for the SGAs. The samples in the present method were directly extracted with 10% acetic acid aqueous solution. The recoveries of SGAs in the potato flesh and skin were in the range of 86.3 to 92.3% and 86.5 to 90.5% with a precision of 2.2 to 4.5% and 3.2 to 5.3%, respectively. The intra- and inter-day validation data for accuracy were in the range of 85.00 to 105.11% with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 1.88 to 8.91% and 98.50 to 100.59% with a CV of 2.11 to 8.22%, respectively. High correlation coefficients (R2 = 0.9997 for α-chaconine and R2 = 0.9996 for α-solanine) were obtained at 2 to 400 μg L−1 SGAs. The results showed that the validation parameters of the method were in the acceptable range as recommended by the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) guidelines. In addition, the SGA contents were significantly higher in the skin than those in the flesh, and significantly increased with time in the skin, but not in the flesh of potato samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...