Amino-functionalized graphene oxide/neutral alumina nanocomposite based solid-phase extraction coupled with ion chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of trace haloacetic acids in drinking water†
Abstract
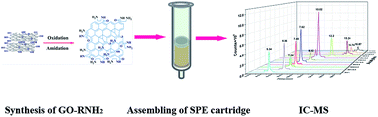
An efficient solid-phase extraction strategy was developed for the extraction and enrichment of ten haloacetic acids from drinking water. An amino-functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposite was synthesized and used as a sorbent. The factors affecting extraction efficiency were optimized by means of the Box–Behnken design. The extracts were analyzed by ion chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (IC-ESI-MS). The combination of extensive sample pretreatment and excellent background suppression was used to effectively eliminate matrix effects that enhanced or suppressed electrospray ionization of analytes. The limits of detection and quantification for ten target compounds were in the range of 0.16–0.61 μg L−1 and 0.55–2.0 μg L−1, respectively. The self-assembled solid-phase extraction cartridge was successfully applied to the enrichment of iodinated, chlorinated and brominated haloacetic acids in sixteen disinfected drinking water samples before detection. Recoveries were between 83.1% and 106.7%, and relative standard deviations ranged from 0.5% to 5.2%. This laboratory-made nanocomposite was proved to be a promising sorbent for the extraction of trace haloacetic acids in water samples.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...