Simultaneous detection of three gynecological tumor biomarkers in clinical serum samples using an ICP-MS-based magnetic immunoassay
Abstract
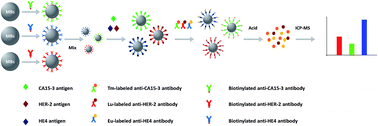
ICP-MS-based multiplex immunoassays have the advantages of low sample consumption and minimized repetitions of tedious procedures. However, this technique is seldom used in clinical tests because of the complicated matrix effect in clinical samples and the discrimination effect to the target proteins. In this work, we developed an ICP-MS-based magnetic immunoassay by using magnetic beads as highly efficient affinity probes and optimizing the magnetic immunoassay parameters. We applied this method to the simultaneous determination of three crucial gynecological tumor biomarkers that are vital in the prognosis and monitoring of the recurrence of breast cancer and ovarian cancer. The measurable ranges of HER-2, HE4 and CA15-3 were 12–1000 ng mL−1, 8–2000 pmol L−1 and 5–200 U mL−1, with detection limits (3σ) of 3.94 ng mL−1, 2.59 pmol L−1 and 1.62 U mL−1, respectively. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) were 2.61% for HER-2 at 15 ng mL−1, 4.90% for HE4 at 25 pmol L−1 and 6.68% for CA15-3 at 10 U mL−1, indicating good accuracy of the method. The spiking test indicated that the present method had a low matrix effect. Under optimized conditions, the simultaneous detection of HER-2, HE4, and CA15-3 in clinical serum samples was performed and the values correlated well with those obtained by the time resolved fluorescence immunoassay (r2 = 0.9568 for HER-2, 0.9485 for HE4, 0.9133 for CA15-3). The present work shows that the ICP-MS-based magnetic immunoassay meets the requirements for the quantification of three crucial gynecological tumor biomarkers in real clinical tests.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...