Detection of small, highly structured RNAs using molecular beacons
Abstract
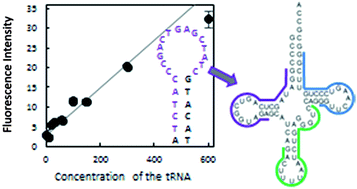
The use of molecular beacons is a versatile method to detect RNAs. Typically, a single-stranded region of RNA is selected as a target sequence for molecular beacons. Therefore, the detection of highly structured short RNAs, such as tRNAs, seems to be difficult. In this study, as an example of highly structured target RNA, we used human tRNALys3, which is known to have functions in protein synthesis and the reverse transcription of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1. No long single-stranded region more than 8 nt is present in this tRNA, which is much shorter than the standard target length of molecular beacons (∼20 nt). This study showed that sensitive detection of highly structured RNAs using molecular beacons was much more difficult than that of unstructured or less structured RNAs. However, efficient detection of the tRNALys3 was achieved by selecting the best target region, i.e., the region around the D arm, probably due to the ease of unfolding of this arm. Accordingly, our findings suggested that molecular beacons may have applications in the detection of highly structured RNAs related to various biological functions and diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...