Increasing flame ionization detector (FID) sensitivity using post-column oxidation–methanation
Abstract
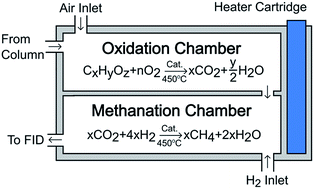
The flame ionization detector (FID) is a robust tool in gas chromatography (GC) due to its sensitivity and linear response in the detection of common organic compounds. However, FID response to oxygenated or highly functionalized organic molecules is low, or in some cases non-existent, making it difficult or impossible to detect and quantify some organic compounds. In this work, the combination of a GC/FID system with a catalytic microreactor, which performs post-column combustion–methanation to convert organic compounds to methane, is shown to be an effective approach for quantifying low-response organic compounds. Molecules that were previously undetectable by conventional FID, including carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, respond with the same high response of methane in the FID. Low-response molecules, including formaldehyde, formic acid, formamide, and ten other oxygenates also demonstrated enhanced detector response equivalent to that of methane in the FID. The linear response of the FID to these molecules and the equivalent sensitivity to methane indicate that accurate quantification is possible without the usual calibration-corrections (e.g., response factors or correction factors) to the FID response.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...