Free-labelled fluorescent method for ATP detection assisted by T4 DNA ligase†
Abstract
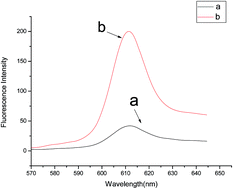
A facile, highly selective biosensor was used for ATP quantitative analysis. Here we introduce two hairpin probes as the matrix. While Exo III digested their duplexes, the blocked G-quadruplex released. Then N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX (NMM) integrated with G-quadruplex to produce strong fluorescence. But when ATP was added, it triggered the T4 DNA ligase to link the two hairpins. As a result, Exo III could not hydrolyze the hairpins leading to a low signal out. With this method, the detection limit reached 3.75 nM, and linear range 5–300 nM for ATP. This method has good selectivity and specificity without a tedious treatment and label process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...