Pd2+ fluorescent sensors based on amino and imino derivatives of rhodamine and improvement of water solubility by the formation of inclusion complexes with β-cyclodextrin†
Abstract
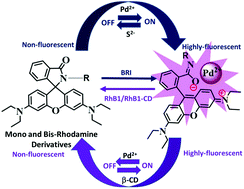
Mono- and bis-rhodamine derivatives appended with amino (RhB1) and imino (BRI) groups, respectively, have been designed as colorimetric and fluorescent sensors for the selective detection of Pd2+. In addition, an attempt has been made to improve the water solubility of the probe by synthesizing inclusion complexes of RhB1 with β-cyclodextrin as the host molecule. The resulting probe, RhB1-CD, exhibited exactly the same physicochemical phenomena as the guest molecule RhB1, indicating that complexation with β-CD improved the water solubility of RhB1 without affecting its sensing ability. With increasing concentrations of Pd2+, the absorption (556 nm) and emission (591 nm) intensities of BRI as well as the absorption intensities of RhB1/RhB1-CD (563 nm) increase, whereas the emission intensities of RhB1/RhB1-CD decrease due to fluorescence quenching. Therefore, BRI can act as an “OFF–ON” fluorescent probe switch in CH3CN/H2O (3 : 2 v/v) with a detection limit of 1 μM in solution, whereas RhB1 and RhB1-CD act as “ON–OFF” fluorescent probes in EtOH/H2O (1 : 1 v/v) and water, respectively, with a detection limit of 10 μM. All these probes exhibited high selectivity for Pd2+ and reversibility by treatment with Na2S. In the presence of commonly coexisting metal ions, such as Hg2+, Fe3+, Cu2+ and Al3+, BRI undergoes either catalytic Schiff base hydrolysis or it is unaffected by its affinity to the metal ions. However, Pd2+ can be effectively distinguished by a 12–15 nm bathochromic shift in its emission spectrum when compared with that of other metal ions. A Job's plot revealed that BRI forms 1 : 2 complexes by a spirolactam ring opening mechanism, whereas RhB1/RhB1-CD form 2 : 1 complexes by a ring opening mechanism followed by Pd2+-induced dimerization; the proposed binding mechanisms are presented.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...