Characterization of peptide attachment on silicon nanowires by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and mass spectrometry†
Abstract
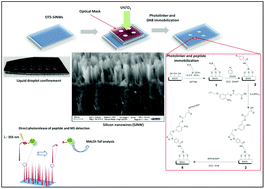
In this paper, we report an original method to immobilize a model peptide on silicon nanowires (SiNWs) via a photolinker attached to the SiNWs’ surface. The silicon nanowires were fabricated by a metal assisted chemical etching (MACE) method. Then, direct characterization of the peptide immobilization on SiNWs was performed either by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) or by laser-desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (LDI-MS). XPS allowed us to follow the peptide immobilization and its photorelease by recording the variation of the signal intensities of the different elements present on the SiNW surface. Mass spectrometry was performed without the use of an organic matrix and peptide ions were produced via a photocleavage mechanism. Indeed, thanks to direct photorelease achieved upon laser irradiation, a recorded predictable peak related to the molecular peptide ion has been detected, allowing the identification of the model peptide. Additional MS/MS experiments confirmed the photodissociation site and confirmed the N-terminal immobilization of the peptide on SiNWs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...