Evaluation of CdTe/CdS/ZnS core/shell/shell quantum dot toxicity on three-dimensional spheroid cultures†
Abstract
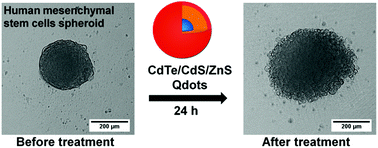
In this work, three-dimensional (3D) spheroid cultures of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAD-MSCs), with tissue-mimetic morphology through well developed cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions and distinct diffusion/transport characteristics, were assessed for dose-dependent toxic effects of red-emitting CdTe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots (Qdots). Morphological investigations and time-resolved microscopy analysis in addition to cell metabolic activity studies revealed that 3D spheroid cultures are more resistant to Qdot-induced cytotoxicity in comparison to conventional 2D cultures. The obtained results suggest the presence of two distinct cell populations in 2D cultures with different sensitivity to Qdots, however that effect wasn't observed in 3D spheroids. Our investigations were aimed to improve the prediction of nanotoxicity of Qdot on tissue-level and provide the essential screening steps prior to any in vivo application. Moreover, penetration ability of highly fluorescent Qdots to densely-packed spheroids will fortify the biological application of developed Qdots in tissue-like structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...