High-dose consumption of NaCl resulted in severe degradation of lipoproteins associated with hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, and infertility via impairment of testicular spermatogenesis†
Abstract
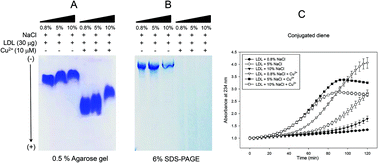
Although the effect of NaCl on serum lipid levels and hypertension is well known, the detailed mechanism of lipoprotein metabolism still remains unclear. To study the physiological effects of high salt consumption on lipoprotein metabolism, NaCl was administered to human cells and zebrafish. Wildtype zebrafish (10-week old) were fed 10% NaCl (wt/wt) in tetrabit diet with or without 4% cholesterol (wt/wt) for 21 weeks. Treatment with NaCl accelerated oxidation and glycation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) as well as induced proteolytic degradation and aggregation. NaCl treatment also exacerbated phagocytosis of oxLDL into macrophage as well as cytotoxicity. The consumption of high salt diet (HSD, final 5% or 10% in diet, wt/wt) supplemented with or without 4% cholesterol for 21 weeks resulted in a remarkable elevation of serum cholesterol, triglyceride, glucose, and hepatic inflammation levels in zebrafish with significant weight loss. Fertility based on egg production was reduced by up to 45% in the HSD group. However, embryonic survivability after hatching was significantly lowered to less than 55%, whereas the control group showed 87% survival. The HSD group showed abnormal testicular histology as well as spermatogenic defects, especially upon the consumption of HCD. These results suggest that hyperlipidemia and high salt consumption have an additive effect on male fertility impairment. High salt consumption exacerbates hyperlipidemia, inflammation, spermatogenic defects, and infertility via a modification of lipoproteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...