Improved efficiency in organic solar cells via conjugated polyelectrolyte additive in the hole transporting layer†
Abstract
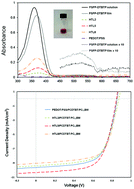
An anionic conjugated polyelectrolyte poly[(9,9-bis(4-sulfonatobutyl sodium) fluorene-alt-phenylene)-ran-(4,7-di-2-thienyl-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole-alt-phenylene)] which exhibits good solubility in water was synthesised via Suzuki-cross coupling. This conjugated polyelectrolyte was used as an additive in the hole transporting layer within organic photovoltaic devices. There is an efficiency gain as a result of an improved carrier generation and charge transport across the interface into the hole transport layer when the work function of the hole transport later is well matched to the active layer of the solar cell. The best performances were achieved using 5 mg ml−1 of the polyelectrolyte additive added to the hole transport layer solution in which case the average power conversion efficiency increased from 4.63% for reference devices without any additive to 5.26% when the additive is present which is a 13% improvement. The reproducibility of device performance was also significantly improved with the variation in fill factor, short circuit current and open circuit voltage all improving when the additive is present.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...