Yellow emitting carbon dots with superior colloidal, thermal, and photochemical stabilities†
Abstract
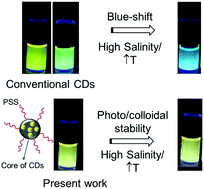
Herein we report the hydrothermal synthesis of yellow emitting carbon dots, CDs, in high salinity water and compare them with those prepared in distilled water. The saline environment significantly affects the surface chemistry and charge of the CDs. We also present data on their long-term colloidal and photochemical stability in distilled and saline water at ambient and high temperatures. The facile preparation and shelf life stability coupled with their improved photochemical and thermal properties make them potential applicants as tracers for biomedical, subsurface and other technologies that require stability under harsh conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...