Highly (100)-oriented sandwich structure of (Na0.85K0.15)0.5Bi0.5TiO3 composite films with outstanding pyroelectric properties
Abstract
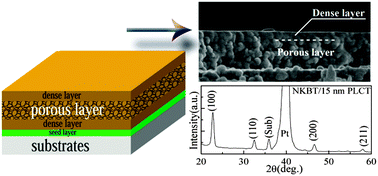
In this paper, by introducing a Pb0.8La0.1Ca0.1Ti0.975O3 (PLCT) seed layer between films and substrates, a dense (Na0.85K0.15)0.5Bi0.5TiO3 (NKBT)/porous NKBT/dense NKBT sandwich structure composite film with high orientation was successfully fabricated at low temperature. The effects of the heating rate on the microstructures and electrical properties of the sandwich structure composite film were investigated in detail. It is found that the porous density of the films increased with decreasing heating rates, and the dielectric constants were significantly decreased. Compared with the sandwich structure NKBT composite films, the sandwich structure NKBT composite films with a seed layer possesses high remnant polarization values and a low leakage current density due to its low-temperature crystallization and high orientation. For the sandwich structure composite film with a seed layer annealed at a heating rate of 20 °C s−1, a low dielectric constant (εr = 110) and a high pyroelectric coefficient (p = 172 µC m−2 K−1) are simultaneously achieved, making great contribution to a higher pyroelectric figure of merit (Fd = 1.3 × 10−5 Pa−1/2) than those of previously reported lead-free pyroelectric films. This work establishes a facile, yet efficient approach to prepare films with a high pyroelectric figure of merit at low temperature, and it extends the possible applications of the sandwich structure films for pyroelectric devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...