Suppression of nanowire clustering in hybrid energy harvesters†
Abstract
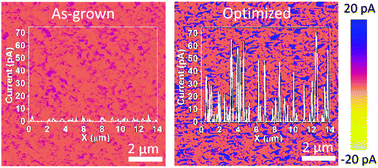
In energy harvesters using arrays of nanowires (NWs), a larger density of NWs should imply higher performance, but in reality the efficiency of the cells is always deteriorated due to NW collision. Impeding the formation of NW clusters in highly populated arrays is essential to ensure effective NW movement and provide a high surface area. Here we present a cost-effective methodology to avoid NW clustering in highly populated arrays of nanowires. First, a flexible polymer is intercalated between the NWs by spin coating, and then its height is tuned by controlled oxygen plasma etching. The resulting optimized energy harvesters show an enhancement in the piezoelectric effect by a factor of 80, as well as a notable improvement in the photoelectric response. The relationship between the height of the intercalated polymer and the piezo potential produced by the nanowires is simulated by the finite element method calculations, which support the experimental observations.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...