The effects of gelatin–dopamine coating on polydimethylsiloxane substrates on pluripotency maintenance and myocardial differentiation of cultured mouse embryonic stem cells†
Abstract
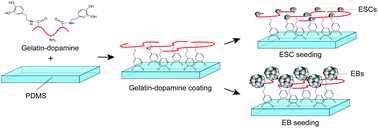
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is a common biomaterial in the fabrication of microfluidic devices due to its various beneficial properties. However, its inherent highly hydrophobic surfaces often limit PDMS-based microfluidic devices for myocardial differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In order to improve cell interactive properties of PDMS, gelatin–dopamine was synthesized by grafting dopamine onto a gelatin backbone. The conjugation of dopamine onto gelatin was verified using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR). Compared with gelatin coating, coating with gelatin–dopamine greatly reduced the water contact angle of the PDMS substrates and resulted in higher protein adsorption on the PDMS surfaces. In addition, the gelatin–dopamine coated PDMS surfaces also improved the embryonic stem cell (ESC) adhesion, proliferation and differentiation as compared to gelatin modified surfaces. The effects of gelatin–dopamine coating on the ESC-derived embryoid body (EB), myocardial differentiation on PDMS surfaces were also investigated. Compared with the PDMS surface coated with gelatin, the EB spread-out areas and myocardial differentiation efficiency greatly increased on the gelatin–dopamine coated PDMS surface. Interestingly, the lower concentration of gelatin–dopamine coating was more favorable for ESC pluripotent maintenance, while the higher concentration was more likely to support ESC myocardial differentiation. These results indicate that gelatin–dopamine is an effective coating material to improve ESC long-term culture and myocardial differentiation on PDMS substrates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...