Red fluorescent probes based on a Bodipy analogue for selective and sensitive detection of selenols in solutions and in living systems†
Abstract
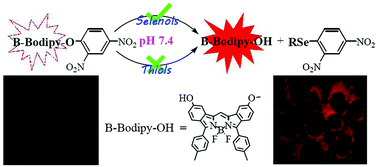
Selenocysteine (Sec), which is a biological selenol incorporated into selenoproteins specifically, plays vital roles in physiological processes and cancer treatment. However, there are limited fluorescent probes for selective detection of Sec and in only one case is a near-infrared (IR) fluorescent probe applied in biological imaging of Sec in living animals. In this work, we have synthesized a new fluorophore, boron-dibenzopyrromethene (B-Bodipy), with an absorption maximum at 650–660 nm, and constructed two deep red fluorescent probes, Sel-p1 and Sel-p2, which are two ethers composed of a 2,4-dinitrobenzenoxy and B-Bodipy moiety. Experiments in solution show that the two probes can react effectively with selenols to release the fluorophore via aromatic nucleophilic substitution (SNAr), with a low limit of detection (16 nM and 9 nM), high selectivity and excellent photostability. The potential application for the detection of Sec in cells has been demonstrated by cell imaging experiments of Sel-p2, including detection of exogenous Sec and selenite-induced Sec in living cells. Furthermore, Sel-p2 as a red fluorescent probe can achieve the detection of Sec in animals by mice imaging experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...