Nanodiamond–PMO for two-photon PDT and drug delivery†
Abstract
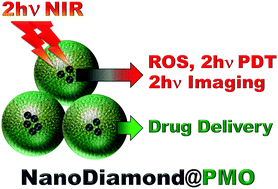
In this article, we highlight the properties of nanodiamonds (ND), which were encapsulated in periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles (PMO) and were able to generate reactive oxygen species for photodynamic applications upon two-photon excitation (TPE). The ND@PMO nanoparticles were characterized by various techniques and were then loaded with the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin. The release of the drug was pH sensitive and a synergistic cancer cell killing effect was observed when cancer cells were incubated with doxorubicin-loaded ND@PMO and irradiated with two-photon excitation at 800 nm.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...