Synthetic self-assembled homogeneous network hydrogels with high mechanical and recoverable properties for tissue replacement†
Abstract
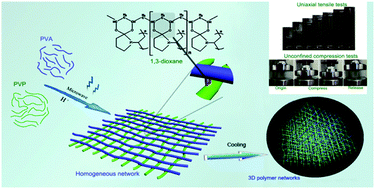
Development of hydrogels with high mechanical and recoverable properties under physiological conditions is of great importance for broadening and improving their potential applications in load-bearing artificial soft tissues. Inspired by the self-assembly of chemical entities, homogeneous network hydrogels, which contain over 90 wt% water, were synthesized via covalent cross-linking of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) triggered by microwave-assisted treatment. A structurally homogeneous network results in an evenly distributed stress that endures high strains with minimal energy dissipation, which enable the hydrogels to withstand up to 1.16 MPa of tensile stress, over seven-fold stretch length with negligible hysteresis, and sustain cyclic compression following high amplitude deformation. It is of importance for tissue replacement that the hydrogels retain these excellent properties under physiological conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...