Effects of thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) on blood coagulation†
Abstract
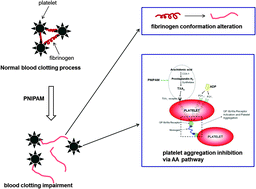
Thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), hydrophilic below its lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of 32 °C and hydrophobic above it, has been widely used as a drug and gene delivery system with intelligent temperature-responsivity. In this work, we studied the in vitro and in vivo effects of PNIPAM on blood coagulation function, and further investigated the interactions of PNIPAM with coagulation-related blood components at cellular and molecular levels. Overall, PNIPAM demonstrated anti-coagulant activity in vitro and in vivo. Specifically, PNIPAM displayed cell membrane activity and caused red blood cell (RBC) aggregation at higher concentrations, but did not impair the membrane integrity of RBCs. PNIPAM inhibited platelet aggregation selectively through the arachidonic acid pathway. PNIPAM also disturbed the structure and conformation of fibrinogen. By contrast, PNIPAM did not affect the activity of the clotting factors in vitro but inhibited the activity of the clotting factors in vivo. The interaction of PNIPAM with plasma proteins was confirmed by a plasma protein absorption study with proteomics analysis. These findings provide key information on the hemocompatibility evaluation and antithrombotic applications of PNIPAM.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...